What are the Common Symptoms of Radiculopathy?
Because of pain, numbness, tingling, and weakness in the arms and legs, people with radiculopathy often have difficulty doing everyday activities. The nerve roots send messages from the brain to the rest of your body, and any damage to them can affect how you move or feel. Some of the most common symptoms of radiculopathy include:
- Tingling or weakness in the arms and legs
- Numbness in the arms and legs
- Decrease in ability to normal movement
- Loss of feeling
- Pain in the neck, shoulders, and back
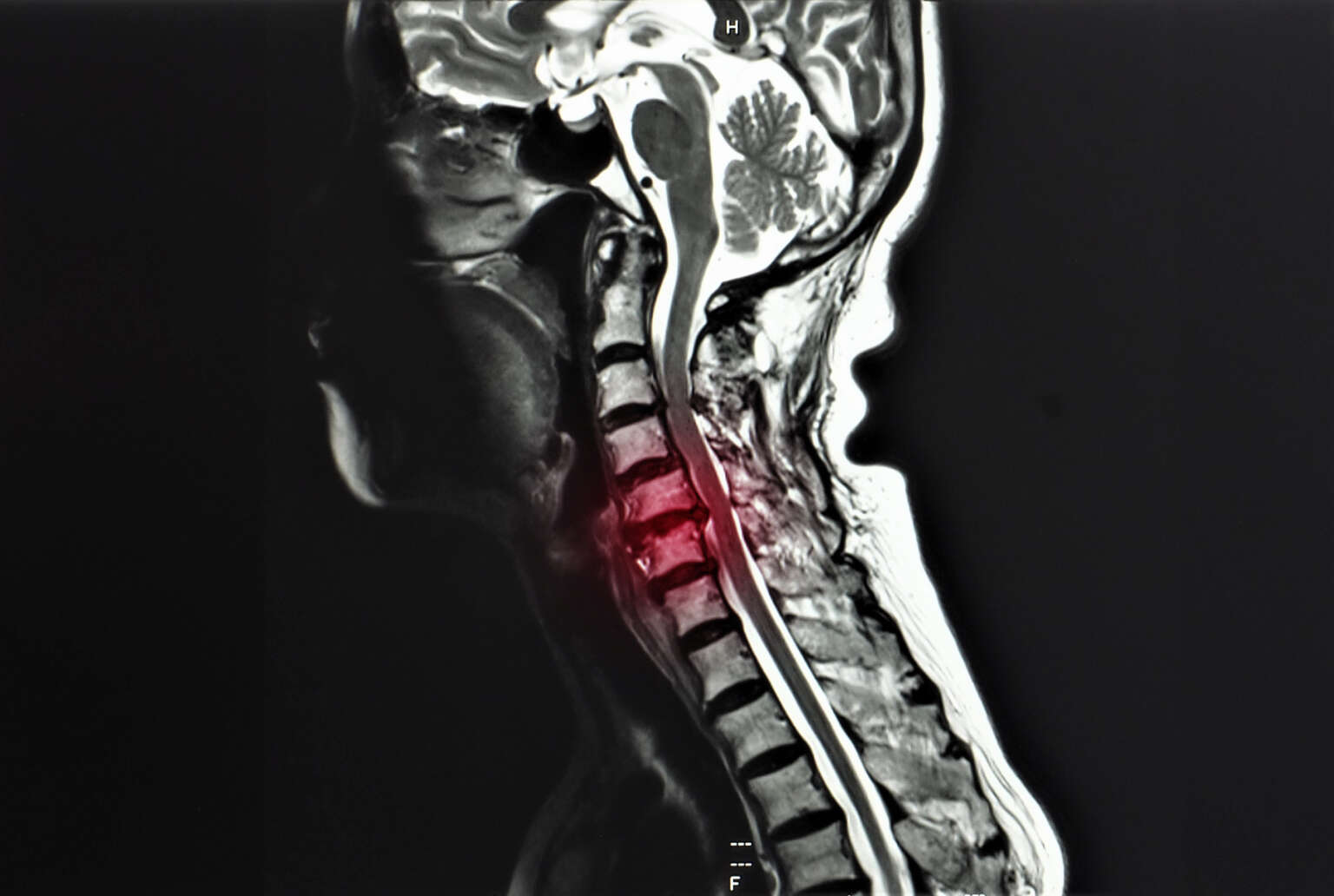
Common Causes of Radiculopathy
The most common cause of radiculopathy is aging. As your body ages, the discs between your vertebrae begin to wear down. This can lead to the disks becoming thin and brittle, which makes them more likely to herniate. Other possible causes of radiculopathy include:
- Arthritis
- Bone spurs
- Tumors on the spine
- Fractures
Known Treatments for Radiculopathy
For Mild Radiculopathy
Pain relievers and anti-inflammatory drugs may be all you need to ease the symptoms. You can also use ice or heat to help relieve the pain. Other medications such as over-the-counter NSAIDs or corticosteroids may be prescribed to help relieve the pain and inflammation. If your radiculopathy is severe, you may need physical therapy to help you regain strength and mobility.
